3 Learning Theories: Understanding How People Learn
Introduction
Learning theories describe the conditions and processes through which learning occurs, providing teachers with models to develop instruction sessions that lead to better learning. These theories explain the processes that people engage in as they make sense of information, and how they integrate that information into their mental models so that it becomes new knowledge. Learning theories also examine what motivates people to learn, and what circumstances enable or hinder learning.
Sometimes people are skeptical of having to learn theory, believing those theories will not be relevant in the real world, but learning theories are widely applicable. The models and processes that they describe tend to apply across different populations and settings, and provide us with guidelines to develop exercises, assignments, and lesson plans that align with how our students learn best. Learning theories can also be engaging. People who enjoy teaching often find the theories interesting and will be excited when they start to see connections between the theory and the learning they see happening in their own classrooms.
General Learning Theories
With a basic understanding of learning theories, we can create lessons that enhance the learning process. This understanding helps us explain our instructional choices, or the “why” behind what and how we teach. As certain learning theories resonate with us and we consciously construct lessons based on those theories, we begin to develop a personal philosophy of teaching that will guide our instructional design going forward. This chapter provides a bridge from theory to practice by providing specific examples of how the theories can be applied in the library classroom. These theories provide a foundation to guide the instructional design and reflective practices presented in the rest of this textbook.
As you read, you might consider keeping track of the key points of each theory and thinking about how these theories could be applied to your practice. Figure 3.1 provides you with an example of a graphic organizer, one of the instructional materials that will be discussed in Chapter 11, that you could use to take notes as you read this chapter. In addition to the examples in practice that are provided in this chapter, you might add some of your own.
Figure 3.1: Graphic Organizer for Major Learning Theories
Behaviorism
Behaviorism is based largely on the work of John B. Watson and B. F. Skinner. Behaviorists were concerned with establishing psychology as a science and focused their studies on behaviors that could be empirically observed, such as actions that could be measured and tested, rather than on internal states such as emotions (McLeod, 2015). According to behaviorists, learning is dependent on a person’s interactions with their external environment. As people experience consequences from their interactions with the environment, they modify their behaviors in reaction to those consequences. For instance, if a person hurts their hand when touching a hot stove, they will learn not to touch the stove again, and if they are praised for studying for a test, they will be likely to study in the future
According to behavioral theorists, we can change people’s behavior by manipulating the environment in order to encourage certain behaviors and discourage others, a process called conditioning (Popp, 1996). Perhaps the most famous example of conditioning is Pavlov’s dog. In his classic experiment, Pavlov demonstrated that a dog could be conditioned to associate the sound of a bell with food, so that eventually the dog would salivate whenever it heard the bell, regardless of whether it received food. Watson adapted stimulus conditioning to humans (Jensen, 2018). He gave an 11-month-old baby a rat, and the baby seemed to enjoy playing with it. Over time, Watson caused a loud, unpleasant sound each time he brought out the rat. Eventually, the baby associated the rat with the noise and cried when he saw the rat. Although Watson’s experiment is now considered ethically questionable, it did establish that people’s behavior could be modified through control of environmental stimuli.
Skinner (1938) examined how conditioning could shape behavior in longer-term and more complex ways by introducing the concept of reinforcement. According to Skinner, when people receive positive reinforcement, such as praise and rewards for certain behaviors, those behaviors are strengthened, while negative reinforcement will deter behaviors. According to Skinner, by carefully controlling the environment and establishing a system of reinforcements, teachers, parents, and others can encourage and develop desired behaviors (Jensen, 2018). A simple example of behaviorism in the classroom is a point system in which students are awarded points for good behavior and deducted points for unwanted behavior. Eventually, accumulated points might be traded in for rewards like small gifts or homework passes. This approach assumes that motivation is external, in that students will engage in certain behaviors in order to gain the rewards.
Because it emphasizes the external environment, behaviorism largely ignores or discounts the role of internal influences such as prior knowledge and emotion (Popp, 1996). To an extent, behaviorists view learners as blank slates and emphasize the role of the teacher in the classroom. In this teacher-centered approach, instructors hold the knowledge, decide what will be learned, and establish the rewards for learning. Since their experience and prior knowledge are not considered relevant, learners are passive participants simply expected to absorb the knowledge transmitted by the teacher. While the idea of learners as blank slates has fallen out of favor, many of the conditioning aspects of behaviorism remain popular. As almost any student can attest, behavioral methods of reinforcement, such as the point system described above, are still common, especially in younger grades. Recent trends toward gaming in the classroom, where certain behaviors are rewarded with points and leveling up, are based in a behaviorist approach to learning. See Activity 3.1 for a brief activity on behaviorism.
Activity 3.1: Reflecting on Behaviorism
Think of some of your own learning experiences, whether they were in a traditional classroom, through professional development training, or related to personal interests, such as dance or photography lessons. Try to identify a few examples of behaviorism from those experiences and reflect on the following questions:
- How did your instructors use behavioral practice in their classrooms?
- Did you find those practices motivating? Why or why not?
- If you can think of examples of behaviorism from several different learning experiences, were they more appropriate in some situations than others? How so?
- Have you ever used, or can you imagine using, behaviorism in your own teaching practice? How so?
Humanism
Humanism recognizes the basic dignity and worth of each individual and believes people should be able to exercise some control over their environment. Although humanism as an educational philosophy has its roots in the Italian Renaissance, the more modern theorists associated with this approach include John Dewey, Carl Rogers, Maria Montessori, Paolo Freire, and Abraham Maslow. Humanist learning theory is a whole-person approach to education that centers on the individual learners and their needs, and that considers affective as well as cognitive aspects of learning. At its essence, “humanism in education traditionally has referred to a broad, diffuse outlook emphasizing human freedom, dignity, autonomy, and individualism” (Lucas, 1996). Within this broader context, humanism is also characterized by the following tenets (Madsen & Wilson, 2012; Sharp, 2012):
- Students are whole people, and learning must attend to their emotional as well as their cognitive state.
- Teachers should be empathetic.
- Learners are self-directed and internally motivated.
- The outcome of learning is self-actualization.
Humanism centers the individual person as the subject and recognizes learners as whole beings with emotional and affective states that accompany their cognitive development. Recognizing the role of students’ emotions means understanding how those emotions impact learning. Student anxiety, say around a test or a research paper, can interfere with the cognitive processes necessary to be successful. Empathetic teachers recognize and try to understand students’ emotional states, taking steps to alleviate negative emotions that might detract from learning by creating a supportive learning environment.
In a library context, Mellon (1986) identified the phenomenon of library anxiety, or the negative emotions that some people experience when doing research or interacting with library tools and services. This anxiety can distract learners and make it difficult to engage in the processes necessary to search for, evaluate, and synthesize the information they need to complete their task. Similarly, in her Information Search Process, Kuhlthau (1990) describes the affective states as well as the cognitive processes students engage in when doing research, acknowledging that their emotions fluctuate among anxiety, optimism, and, ultimately, satisfaction or disappointment.
A humanist approach to education recognizes these affective states and seeks to limit their negative impact. For instance, we can acknowledge that feelings of anxiety are common so learners recognize that they are not alone. We can also explain how the skills students learn are relevant to their lives in and outside of the classroom.
Because humanists see people as autonomous beings, they believe that learning should be self-directed, meaning students should have some choice in what and how they learn. Humanistic education is often connected with student-centered pedagogical approaches such as differentiated curricula, self-paced learning, and discovery learning (Lucas, 1996). Self-directed learning can take many forms, but it generally means that the instructor acts as a guide, and learners are given the freedom to take responsibility for their own learning. Teachers will provide the materials and opportunities for learning, but students will engage with the learning on their own terms. In a library classroom, we can give students choices about the topics they will research or offer learners different types of activities to practice skills and demonstrate what they have learned.
Humanists also believe that learning is part of a process of self-actualization. They maintain that learning should be internally motivated and driven by students’ interests and goals, rather than externally motivated and focused on a material end goal such as achievement on tests, or employment (Sharp, 2012). The expectation is that when students are allowed to follow their interests and be creative, and when learning takes place within a supportive environment, students will engage in learning for its own sake. This emphasis on self-actualization is largely based on Maslow’s (1943) hierarchy of needs. Maslow identified five levels of needs: basic physiological needs such as food, water, and shelter; safety and security needs; belongingness and love needs, including friends and intimate relationships; esteem needs, including feelings of accomplishment; and self-actualization, when people achieve their full potential. Importantly, these needs are hierarchical, meaning a person cannot achieve the higher needs such as esteem and self-actualization until more basic needs such as food and safety are met. The role of the humanist teacher is to facilitate the student’s self-actualization by helping to ensure needs such as safety and esteem are met through empathetic teaching and a supportive classroom.
In his book, Pedagogy of the Oppressed, Freire (2000) brings together many of the student-centered elements of humanistic education, with a strong emphasis on social justice aspects of learning and teaching. In contrast to behaviorist approaches, Freire emphasizes the importance of students’ life experience to their learning. He criticizes what he describes as the “banking model” of education, in which students are viewed as passive and empty vessels into which teachers simply deposit bits of knowledge that students are expected to regurgitate on exams or papers without any meaningful interaction. Freire insists that learning must be relevant to the student’s life and the student should be an active participant in order for learning to be meaningful. Freire also emphasized the emancipatory role of education, arguing that the purpose of education was for learners to gain agency to challenge oppressive systems and improve their lives, and praxis, in which learners put abstract and theoretical knowledge into practice in the real world.
While a student-centered approach and choice can be introduced in any classroom, observers note that in an age of curriculum frameworks and standardized tests, where teachers are often constrained by the material, the ability to provide students with choice and allow for exploration is limited (Sharp, 2012; Zucca-Scott, 2010). Librarians often face similar constraints. School librarians also must meet state and district curriculum standards. Academic librarians generally depend on faculty invitations to conduct instruction and need to adapt their sessions to fit the content, time frame, and learning objectives of the faculty member. Nevertheless, we can always find ways to integrate some self-direction. For instance, rather than using planned examples to demonstrate searches, we might have students suggest topics to search. If we plan hands-on practice activities, we could allow learners to explore their own interests as they engage in the activity, rather than limiting them to preselected topics.
Cognitivism
Cognitivism, or cognitive psychology, was pioneered in the mid-twentieth century by scientists including George Miller, Ulric Neisser, and Noam Chomsky. Whereas behaviorists focus on the external environment and observable behavior, cognitive psychologists are interested in mental processes (Codington-Lacerte, 2018). They assert that behavior and learning entail more than just response to environmental stimuli and require rational thought and active participation in the learning process (Clark, 2018). To cognitivists, learning can be described as “acquiring knowledge and skills and having them readily available from memory so you can make sense of future problems and opportunities” (Brown et al., 2014, p. 2).
Cognitivists view the brain as an information processor somewhat like a computer that functions on algorithms that it develops in order to process information and make decisions. According to cognitive psychology, people acquire and store knowledge, referred to as schema, in their long-term memory. In addition to storing knowledge, people organize their knowledge into categories, and create connections across categories or schema that help them retrieve relevant pieces of information when needed (Clark, 2018). When individuals encounter new information, they process it against their existing knowledge or schema in order to make new connections. Cognitivists are interested in the specific functions that allow the brain to store, recall, and use information, as well as in mental processes such as pattern recognition and categorization, and the circumstances that influence people’s attention (Codington-Lacerte, 2018).
Because cognitivists view memory and recall as the key to learning, they are interested in the processes and conditions that enhance memory and recall. According to cognitive psychology research, traditional methods of study, including rereading texts and drilling practice, or the repetition of terms and concepts, are not effective for committing information to memory (Brown et al., 2014). Rather, cognitivists assert that activities that require learners to recall information from memory, sometimes referred to as “retrieval practice,” lead to better memory and ultimately better learning. For example, they suggest that language learners use flash cards to practice vocabulary words, rather than writing the words out over and over or reading and rereading a list of words, because the flash cards force the learner to recall information from memory.
While testing has fallen out of favor with many educators and education theorists, cognitivists find tests can be beneficial as both a retrieval practice and a diagnostic tool. They view tests not only as a way to measure what has been learned but as a way to practice retrieval of important concepts, and as a way to identify gaps or weaknesses in knowledge so that learners know where to concentrate their efforts (Brown et al., 2014). Cognitivists encourage “spaced practice,” or recalling previously learned information at regular intervals, and “interleaving,” or learning related concepts together to establish connections among them. Their research has found that retrieval is more effective when the brain is forced to recall information after some time has passed, and when the recall involves two or more related subjects or concepts. Finally, cognitivists also promote problem-based learning, maintaining that “trying to solve a problem before being taught the solution leads to better learning, even when errors are made in the attempt” (Brown et al., 2014, p.4).
These processes that enhance memory and recall, and thus learning, have some implications for instructors in creating an optimal environment for learning. Gagné (1985) proposed nine conditions for learning, referred to as the external conditions of learning, or the nine events of instruction:
- Gain attention. Engage students’ attention by tying learning to relevant events in their lives and asking stimulating questions.
- Inform the learner of the objective. Begin by sharing the learning goals with the students, thus setting expectations and providing a map of the learning.
- Stimulate recall of prior learning. Encourage students to remember previously learned relevant skills and knowledge before introducing new information.
- Present the stimulus. Share new information. This step depends on the content of the lesson. For instance, a lesson on Boolean operators might begin with a Venn diagram and examples of the uses of and, or, and not.
- Provide learner guidance. Facilitate learning by demonstration and explanation.
- Elicit performance. Allow time for students to practice skills and demonstrate their abilities. Ideally, students would be given low-stakes opportunities for practice, so they feel comfortable if they do not succeed immediately.
- Provide feedback. Offer students input on what they are doing well and where they can improve.
- Assess performance. Employ measures such as assignments, activities, and projects to gauge whether learning has occurred.
- Enhance retention and transfer. Give students opportunities to practice skills in new contexts, which improves retention and helps students see how the skills are applied to different areas.
Cognitivism remains a popular approach to learning. However, one criticism of cognitive psychology is that, unlike humanism, it does not account for the role of emotions in learning (Codington-Lacerte, 2018). Further, some critics believe that cognitivism overemphasizes memorization and recall of facts to the detriment of higher-order skills such as creativity and problem solving. However, cognitivists argue that the ability to recall facts and concepts is essential to higher-order thinking, and therefore the two are not mutually exclusive but actually interdependent (Brown et al., 2014). Finally, cognitivism is considered teacher-centered, rather than learner-centered, since it emphasizes the role of the instructor in organizing learning activities and establishing the conditions of learning (Clark, 2018). Activity 3.2 is a brief exercise on cognitivism.
Activity 3.2: Reflecting on Cognitivism
Cognitive scientists recommend retrieval practice, including spaced practice and interleaving, over drilling.
Questions for Reflection and Discussion:
- What kind of study practices do you tend to use? Do your practices vary depending on the content or material you are studying? How so?
- Can you think of ways to integrate retrieval practices into your work for this class?
- Spaced practice involves returning to previously learned concepts at later times, but information professionals often teach one-shot sessions. Can you think of ways to integrate spaced practice into a one-shot session?
Constructivism
Constructivism posits that individuals create knowledge and meaning through their interactions with the world. Like cognitivism, and as opposed to behaviorism, constructivism acknowledges the role of prior knowledge in learning, believing that individuals interpret what they experience within the framework of what they already know (Kretchmar, 2019a). Social constructs, such as commonly held beliefs, and shared expectations around behavior and values provide a framework for knowledge, but people “do not just receive this knowledge as if they were empty vessels waiting to be filled. Individuals and groups interact with each other, contributing to the common trove of information and beliefs, reaching consensus with others on what they consider is the true nature of identity, knowledge, and reality” (Mercadal, 2018). Cognitivism and constructivism overlap in a number of ways. Both approaches build on the theories of Jean Piaget, who is sometimes referred to as a cognitive constructivist. However, while cognitivism is considered teacher-centered, constructivism centers the learner by recognizing their role in engaging with content and constructing meaning. Constructivist teachers act as guides or coaches, facilitating learning by developing supportive activities and environments, and building on what students already know (Kretchmar, 2019b).
Piaget discusses the concepts of assimilation, accommodation, and disequilibrium to describe how people create knowledge. In his early work as a biologist, Piaget noticed how organisms would adapt to their environment in order to survive. Through such adaptation, the organism achieved equilibrium. Extending these observations to cognitive science, he posited that human beings also seek equilibrium (Kretchmar, 2019a).
When they encounter new situations, or new information, human beings must find a way to deal with the new information. Similar to the processes described in the section on cognitivism, people will examine their existing knowledge, or schema, to see if the new information fits into what they already know. If it does, they are able to assimilate the information relatively easily. However, if the new information does not fit into what people already know, they experience disequilibrium or cognitive conflict, and must adapt by accommodating the new information. For example, once children learn what a dog is, they might call any four-legged creature they see a dog. This is assimilation, as the children are fitting new information into their existing knowledge. However, as children learn the differences between, say, a dog and cat, they can adjust their schema to accommodate this new knowledge (Heick, 2019).
Disequilibrium and accommodation can be uncomfortable. People might be confused or anxious when they encounter information that does not fit their existing schema, and they might struggle to accommodate that new information, but disequilibrium is crucial to learning (Kretchmar, 2019a). During assimilation, people might be adding new bits of information to their knowledge store, but they are not changing their understanding of the world. During accommodation, as people change their schema, construct new knowledge, and draw new connections among existing areas of knowledge, actual learning occurs, and accommodation requires disequilibrium.
Acknowledging the role of disequilibrium is important for both instructors and students. People naturally want to avoid discomfort, but that can also mean avoiding real learning. As instructors, we can facilitate accommodation by acknowledging that the process might be challenging, and by creating conditions that allow students to feel safe exploring new information. We can reassure learners that feelings of discomfort or anxiety are normal and provide them with low-stakes opportunities to engage with new information.
Social Constructivism
Social constructivism builds on the traditions of constructivism and cognitivism; whereas those theories focus on how individuals process information and construct meaning, social constructivists also consider how people’s interactions with others impact their understanding of the world. Social constructivists recognize that different people can have different reactions and develop different understandings from the same events and circumstances, and are interested in how factors such as identity, family, community, and culture help shape those understandings (Mercadal, 2018).While cognitivists and constructivists view other people as mostly incidental to an individual’s learning, social constructivists see community as central. Social constructivism can be defined as “the belief that the meanings attached to experience are socially assembled, depending on the culture in which the child is reared and on the child’s caretakers” (Schaffer, 2006). Like constructivism, social constructivism centers on the learners’ experiences and engagement, and sees the role of the instructor as a facilitator or guide. Two of the major theorists associated with social constructivism are Pierre Bourdieu and Lev Vygotsky.
Vygotsky built on the work of Piaget and believed knowledge is constructed, but felt that prior theories overemphasized the role of the individual in that construction of knowledge. Instead, he “was most interested in the role of other people in the development and learning processes of children,” including how children learn in cooperation with adults and older or more experienced peers who can guide them with more complex concepts (Kretchmar, 2019b). Vygotsky was also interested in how language and learning are related. He postulated that the ways in which people communicate their thoughts and understandings, even when talking themselves through a concept or problem, are a crucial element of learning (Kretchmar, 2019b). For Vygotsky, interaction and dialogue among students, teachers, and peers are key to how learners develop an understanding of the world and of the socially constructed meanings of their communities.
Bourdieu examined the way in which social structures influence people’s values, knowledge, and beliefs, and how these structures often become so ingrained as to be invisible. People within a society become so enculturated into the systems and beliefs of that society that they often accept them as “normal” and do not see them as imposed structures (Roth, 2018). As a result, individuals might not question or challenge those structures, even when they are unfair or oppressive. In addition to examining how community and culture help shape knowledge, Bourdieu was interested in how issues of class impact learning. He observed that over time, schools developed to reflect the cultures of wealthier families, which enabled their children to succeed because they inherently understood the culture of the classroom and the system of education. We continue to see such issues today, and as discussed more in Chapter 5 and Chapter 6, part of our critical practice is to ensure that our classrooms and instructional strategies are inclusive of and responsive to all students.
Activity 3.3 explores how we can use theory to guide our practice.
Activity 3.3: Using Learning Theory to Plan Lessons
While learning theories can be interesting on their own, our goal as instructors is to apply them to classroom practice. Imagine that you are a high school librarian working with a class that has just been assigned a research paper. Your goal for this session is for students to brainstorm keywords and synonyms for their topics, and to learn how to string those words together using the Boolean operators and, or, and not. You want to be sure the students understand the function of the Boolean operators and can remember how to use them for future searches.
Choose one of the learning theories outlined in this chapter and design a brief lesson to teach Boolean operators from the perspective of that theory. Concentrate less on what you would teach but rather on how you would teach it in keeping with the chosen theory:
- How would you introduce the topic?
- What sort of learning activities would you use?
- What would you be doing during the lesson? What would you expect students to do?
- How might any of your answers to these questions change if you were to use a different theory as your guide?
Developmental Stages
The learning theories outlined above discuss various cognitive processes involved in learning, as well as some of the motivators and conditions that facilitate learning. While these theories attempt to describe how people learn, it is important to note that individuals are not born ready to engage in all of these processes at once, nor do they necessarily all engage in the same processes at the same time. Rather, more complex processes develop over time as people experience the world and as their brain matures. In addition to studying how people learn, some theorists have also proposed theories or frameworks to describe developmental stages, or the various points in human development when different cognitive processes are enabled, and different kinds of learning can occur.
Piaget outlined four hierarchical stages of cognitive development: sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational (Clouse, 2019), illustrated in Table 3.1. In the sensorimotor stage, from birth to about two years, infants react to their environment with inherent reflexes such as sucking, swallowing, and crying. By about age two, they begin problem solving using trial and error. The preoperational stage, also sometimes called the intuitive intelligence stage, lasts from about ages two to seven. During this time, children develop language and mental imagery. They are able to use their imagination, but they view the world only from their own perspective and have trouble understanding other perspectives. Their understanding of the world during this stage is tied to their perceptions. Children are in the operational stage from about ages seven to 12, during which time they begin to think more logically about the world, can understand that objects are not always as they appear, and begin to understand other people’s perspectives. The final stage, formal operationalism, begins around age 12. At this point, individuals can think abstractly and engage in ideas that move beyond the concrete world around them, and they can use deductive reasoning and think through consequences (Clark, 2018; Clouse, 2019).
Table 3.1: Piaget’s Four Stages of Cognitive Development
| Stage | Age Range | Behaviors and Abilities |
| Sensorimotor | Birth to 18-24 months |
|
| Preoperational | 18-24 months to 7 years |
|
| Concrete operational | 7 to 12 years |
|
| Formal operational | 12 years and up |
|
Perry’s (1970) Scheme of Intellectual and Moral Development offers another useful framework for understanding the developmental stages of learning. Perry proposed four stages of learning. In the first stage, dualism, children generally believe that all problems can be solved, and that there are right and wrong answers to each question. At this stage, children generally look to instructors to provide them with correct answers. The second stage is multiplicity, where learners realize that there are conflicting views and controversies on topics. Learners in the multiplicity stage often have trouble assessing the authority and credibility of arguments. They tend to believe that all perspectives are equally valid and rely on their own experiences to form opinions and decide what information to trust. In the next stage, referred to as relativism, learners begin to understand that there are different lenses for understanding and evaluating information. They learn that different disciplines have their own methods of research and analysis, and they can begin to apply these perspectives as they evaluate sources and evidence. At this point, learners can understand that not all answers or perspectives are equal, but that some answers or arguments might be more valid than others. In the final stage, commitment, students integrate selected information into their knowledge base. You might notice connections between Perry and the cognitivists and constructivists described above in the way they each describe people making sense of information by comparing new information to existing knowledge. However, Perry organizes the processes into developmental stages that outline a progression of learning.
Understanding the stages laid out by Piaget and Perry, we can develop lessons that are appropriate to learners at each stage. For example, in presenting a lesson on climate change to preoperational students using Piaget’s framework, an instructor could gather pictures of different animal habitats, or take children on a nature walk to observe the surrounding environment. Instructors could ask these children to describe what they see and reflect on their personal experiences with weather, while older children could be asked to imagine how the changes are impacting other people and organisms, anticipate consequences of the impact of climate change, and perhaps use problem solving to propose steps to improve their environment. Considering Perry’s Scheme, instructors might guide students from multiplicity to relativism by explaining scientific methods for measuring climate, and challenging learners to evaluate and compare different sources of information to determine which presents the strongest evidence.
Piaget and Perry offer developmental models that outline stages broadly aligned with a person’s age. Both models assume a relatively linear chronological development, with children and young adults passing through different stages at roughly the same time. Vygotsky, on the other hand, describes a model that focuses more on the content being mastered rather than the age of the student. According to Vygotsky’s theory, known as Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD), as learners acquire new knowledge or develop new skills, they pass through three stages, often illustrated as concentric circles, as in Figure 3.2. The center circle, or first zone, represents tasks that the learner can do on their own. The second zone, or the Zone of Proximal Development, represents an area of knowledge or set of tasks that the learner can accomplish with assistance. The tasks and knowledge in this zone require students to stretch their abilities somewhat beyond their current skill level but are not so challenging as to be completely frustrating. The outermost circle, or third zone, represents tasks that the learner cannot yet do. Vygotsky posits that by working within the ZPD, learners can continue to grow their skills and abilities and increase their knowledge (Flair, 2019).
Figure 3.2: The Zone of Proximal Development
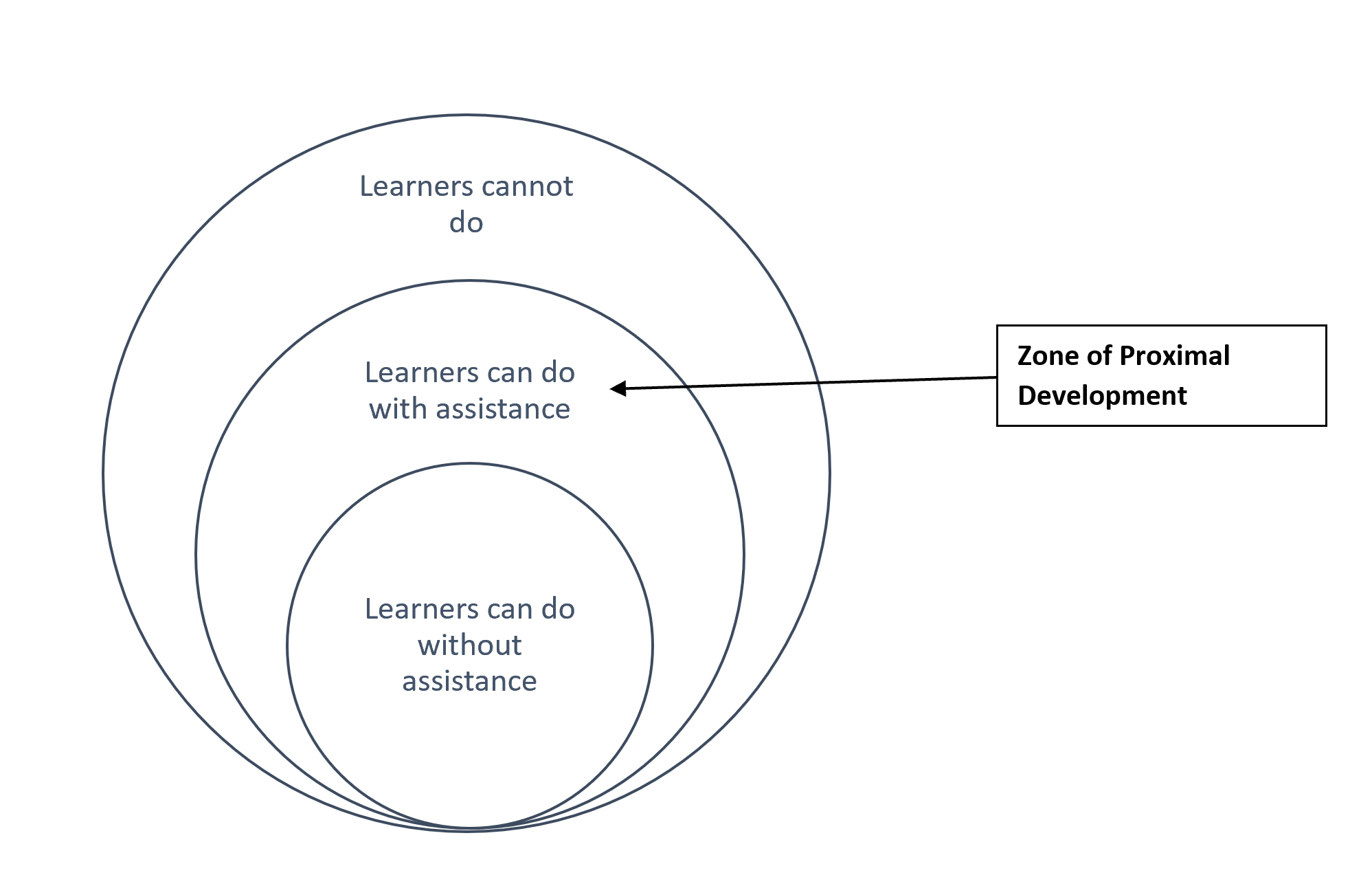
Whereas Piaget and Perry’s theories suggest that learners pass through the same stages at roughly the same time, Vygotsky maintains that the ZPD, or the zone of learning that will appropriately challenge the learner, is different for each student, depending on their background knowledge, experience, and ability (Flair, 2019). The same individual can experience different ZPDs in different subject areas; they might be advanced in math and able to take on material above their grade level but might find languages more challenging. Like with social constructivism, interaction with others is central to ZPD. According to Vygotsky, learning takes place when students interact with others who are more knowledgeable, including peers and instructors, who can provide guidance in the ZPD (Schaffer, 2006).
Math can provide a good example of working within the ZPD. Once students are comfortable with addition, they can probably learn subtraction with some help from a teacher or other peers but are probably not ready to learn long division. Our challenge as instructors is to identify the ZPD for each student so that we are neither boring learners with material that is too easy nor overwhelming them with material that is too hard. Chapter 7 discusses methods for assessing learners’ background knowledge to help determine the appropriate level of learning.
Andragogy
Most of the educational theories and frameworks outlined in this chapter were developed with a focus on children and young adults. While many of the principles can apply to an adult audience, they do not necessarily account for the specific issues, challenges, and motivations of adult learners. Yet, many information professionals will work mostly or even exclusively with adults. Academic librarians and archivists largely work with students who are at least 17 years old and, as the numbers of nontraditional students continue to increase, will find themselves increasingly working with older learners. Likewise, information professionals in corporations and medical and legal settings work almost exclusively with adults. Public librarians see a range of patrons, and many public libraries are increasing educational programming for their adult patrons. This section presents the educational concept of andragogy, which addresses teaching and learning for adults.
Knowles proposed andragogy as “the art and science of helping adults learn” (1988, p. 43). Andragogy is based on a set of assumptions about the ways in which adult learners’ experience, motivations, and needs differ from those of younger students, and suggests that traditional classroom approaches developed with younger students in mind will not necessarily be successful with adult learners. Perhaps one of the biggest differences between child and adult learners, according to Knowles (1988), is that adults are interested in the immediate applicability of what they are learning and are often motivated by their social roles as employees, parents, and so on. As Knowles notes, in traditional classrooms, children are usually taught discrete subjects like math, reading, and history, and their learning is focused on building up knowledge for the future. Young students might not use geometry in their everyday lives, but it forms a foundation for more complex math and for future job or life tasks like measuring materials for home repairs.
Adults, on the other hand, are already immersed in the social roles for which younger students are only preparing, and they want to see how their learning applies to those roles. Thus, Knowles suggests that adults will be interested in a competency-based, rather than a subject-based, approach to learning. Further, as autonomous individuals, adults are likely to be more self-directed in their learning. That is, they will want to, and should be encouraged to, take an active part in the design and planning of lessons, providing input on content and goals. Finally, Knowles also argues that adults’ wider experience and larger store of knowledge should be a resource for learning.
Knowles (1988, p. 45) organized his approach around four assumptions of adult learners:
- Their self-concept moves from one of being a dependent personality toward a self-directed human being.
- They accumulate a growing reservoir of experience that becomes an increasingly rich resource for learning.
- Their readiness to learn becomes oriented increasingly to the developmental tasks of their social roles.
- Their time perspective changes from one of postponed application of knowledge to immediacy of application, and, accordingly, their orientation toward learning shifts from one of subject-centeredness to one of performance-centeredness.
Later, he elaborated with two additional assumptions, summed up by Merriam et al. (2007):
- The most potent motivations are internal rather than external.
- Adults need to know why they need to learn something.
Certain understandings follow from Knowles’ assumptions that we can use to guide our practice with adult learners. To begin with, we should recognize and respect adults’ tendency to be self-motivated and self-directed learners. After all, in most states, school attendance is compulsory up to a certain age, and relatively strict curriculum standards are set by each state, meaning that children have little choice about attending school in some form or about what content they learn. At least in theory, adults have a choice about whether to attend college or engage in other kinds of learning opportunities such as workshops and professional development and continuing education courses. Presumably, adults are motivated to pursue these opportunities for a specific reason, whether out of personal curiosity, to advance in their careers, or to gain a new skill. These adult learners will likely have opinions and ideas about what they want to learn and perhaps even how they want to engage with the content, so Knowles suggests we provide adult learners with choices and opportunities for input to help shape the curriculum.
Adult learners also have a larger store of knowledge and experience than their younger counterparts. From a cognitivist or constructivist point of view, adults have a larger schema against which to compare new information and make new connections. As instructors, we should recognize this store of knowledge and find ways to integrate it into the classroom, by providing ample opportunity for reflection and using guiding questions to encourage learners to draw on that knowledge. We can approach adult learners as peers or co-learners, acting more as coaches or facilitators in the learning process than as the more directive teacher associated with a traditional school classroom. This focus on learner-centered approaches and a democratic environment overlaps with humanistic and constructivist approaches to teaching.
Points three, four, and six in Knowles’ list of assumptions underscore the importance of relevance and transparency for adult learners. Knowles suggests that adults have different priorities in learning, perhaps in part because they are learning by choice and are in a better position to direct their own learning. Adult learners also tend to have more demands on their time than younger students; they may have families and jobs that impact the time they have to devote to their studies. Thus, adult learners want to see the applicability of what they are learning and might be resistant to work or information that seems incidental. We should be transparent with our adult students, both about what they will learn and how that learning is important and relevant. Sharing learning goals is an important step toward transparency, as it can help set expectations so that students understand the purpose of the lesson and activities. To illustrate relevance, we can provide concrete examples of how the learning can be applied in practice. One could argue that all students, not just adults, deserve transparency and to see the relevance of lesson goals and learning. Knowles’ point is that adults are more likely to expect, and perhaps appreciate, such transparency.
While some controversy exists over whether andragogy really constitutes a theory per se or is more a set of guiding principles or best practices, the assumptions provide helpful guidance to instructors not just in how they organize content but also in how they frame the lesson and its purposes. Based on these assumptions, we can take certain steps to set an appropriate environment for adult education (Bartle, 2019):
- Set a cooperative learning climate.
- Create mechanisms for input.
- Arrange for a diagnosis of learner needs and interests.
- Enable the formulation of learning objectives based on the diagnosed needs and interests.
- Design sequential activities for achieving the objectives.
- Execute the design by selecting methods, materials, and resources.
- Evaluate the quality of the learning experience while rediagnosing needs for further learning.
As noted above, andragogy overlaps with other theories such as humanism and constructivism, and some of the principles of andragogy, like transparency, would benefit all learners. Still, this framework is useful in reminding instructors that adult learners likely have different priorities and motivations, and thus some differences in classroom approach might be warranted.
Motivation
In addition to how people learn, we should also know something about why people learn. What motivates a student to put the time and effort into learning a skill or topic, and what can we do to cultivate that motivation? Svinicki (2004) offers an intriguing model that amalgamates some of the prevailing theories of motivation in learning. She suggests that motivation is a factor of the perceived value of the learning, along with students’ belief in their own self-efficacy, or their belief in their ability to achieve the goal. As Svinicki explains, “motivation involves a constant balancing of these two factors of value and expectations for success” (2004, p. 146). Most of the learning theories outlined above address motivation implicitly or explicitly. For instance, behaviorists talk in terms of reinforcement, or external motivators, as students strive to avoid negative consequences and achieve the rewards of good work. Humanists, on the other hand, focus on the internal motivation of self-actualization. As instructors, we can create environments to increase our learners’ motivation or their perception of the value of the goal and their self-efficacy:
- Emphasize the relevance of the material. As outlined in the section on andragogy, learners are motivated when they see the benefits of learning and understand why the material is important. Instructors should explain how the effort individuals put into learning can help them achieve personal goals, such as getting a good grade on a paper or finding a job.
- Make the material appropriately challenging. Reminiscent of the Zone of Proximal Development, material that is too easy will be boring for learners, while material that is too challenging will be overwhelming and frustrating.
- Give learners a sense of choice and control. Choice allows learners to have a stake in the class, while control helps them determine the level of risk they will take and thus increase their confidence. We can foster choice and control by allowing learners options in the types of activities and assignments they engage in, or in the topics they research.
- Set learners up for success. Clear expectations for the class or the assignment help learners understand what a successful performance or project looks like. By providing meaningful feedback, we can guide learners toward success.
- Guide self-assessment. When learners accurately assess their current level of knowledge and skill, they can make reasonable predictions of the likelihood of their success with the current material.
Activity 3.4 offers an opportunity to reflect on motivation in learning.
Activity 3.4: What Motivates You?
Think back on learning experiences such as courses or workshops where you felt more or less motivated as a learner. These experiences could be related to academics, hobbies, sports, or other interests.
Questions for Reflection and Discussion:
- In the experiences in which you felt motivated, what steps did the instructor take that helped you feel motivated?
- In the experiences where you felt less motivated, what could the instructor have done differently?
- In each case, what role did self-efficacy, or your confidence in your own abilities, play?
Growth Mindset
Dweck’s (2016) mindset theory has gained much attention in the field of education over the last few decades and has some implications for student motivation. Although this theory is somewhat different in its conceptualizations than those described in the rest of this chapter, it is included here both because of its popularity and because it provides interesting insight into how instructors can coach learners to understand and build on their potential. Dweck’s theory is less about how people learn and more about how their attitude toward learning and their self-concept can impact their ability and willingness to learn. According to Dweck, people tend to approach learning with a fixed mindset or a growth mindset. Those with more of a fixed mindset tend to believe that ability is innate; either people are born with a certain talent and ability, or they are not. If individuals are not born with natural ability in a certain area, they would waste time working on that area because they will never truly be successful. People with more of a growth mindset, on the other hand, tend to believe that ability is the outcome of hard work and effort. These people see value in working at areas in which they are not immediately successful because they believe they can improve. Even when they are good at something, they are willing to continue to work at it because they believe they can continue to get better (Dweck, 2016).
These mindsets can have a profound impact on how a person approaches learning (Dweck, 2016). People with a fixed mindset will view low grades or poor test performance as a sign of their lack of natural ability and are likely to become discouraged. They might try to avoid that subject altogether or resign themselves to failure because they do not believe that practice or study will help them improve. Instead, they will tend to stick to subjects in which they already perform well. People with a growth mindset take an opposite view. They tend to view low grades or poor performance as a diagnostic tool that helps them see where they need to concentrate their efforts in order to get better. They are willing to put in extra effort because they believe that their hard work will lead to improved performance. They are also willing to take risks because they understand that failure is just part of the process of learning. We can see connections between Dweck’s theory and Piaget’s argument that the discomfort of disequilibrium is necessary to learning.
Understandably, people with a growth mindset are usually more successful learners because they believe in their own ability to learn and grow. Luckily, Dweck maintains that these mindsets themselves are not necessarily immutable. That is, a person with a fixed mindset can be coached to adopt a growth mindset. Learners can begin by recognizing when they are engaging in fixed mindset thinking, for instance when getting anxious about mistakes or telling themselves that they are “no good” at something. Once learners understand that this thinking is counterproductive, they can change their thinking to adopt a more encouraging voice.
Importantly, Dweck notes that encouraging a growth mindset in the classroom does not mean lowering standards for learning. She maintains that instructors should have high standards but also create a supportive and nurturing atmosphere. To begin with, instructors themselves must believe that learning and growth are possible, and not give up on students who are struggling. Instructors can model this belief for students by replacing fixed mindset feedback with growth mindset feedback. For example, Dweck suggests that if learners are struggling, instructors can respond by telling them they have not succeeded yet. The word “yet” implies that they will achieve the necessary learning; they just need to keep working at it. In that way, instructors can reframe mistakes and struggles as opportunities to learn rather than as failures. Instructors should encourage and appreciate effort as well as learning. In other words, rather than focusing only on a student’s achievement, instructors can praise the effort and hard work that led to that achievement. At the same time, Dweck (2015) notes that a growth mindset is not just about effort. In addition to putting in the work, learners must also be willing to try different strategies and be open to feedback on their performance. The goal is to help students view challenges as part of the learning process and to work with them rather than to fear or avoid them.
Conclusion
Learning theories are meant to help instructors understand the processes and circumstances that enable learning and, by extension, offer guidance in developing activities and environments that best support learning. But what to make of the fact that there are so many different theories and that some contradict each other? The truth is that the human brain and its cognitive processes are incredibly complex and not yet fully understood. Learning theorists do their best to describe how people learn based on careful observation and experimentation, but no learning theory is perfect. Indeed, each theory has its critics, and the various theories go in and out of favor over time. Even so, the theories provide us with an empirically based understanding of how learning occurs.
Further, these theories are not mutually exclusive. We do not have to strictly adhere to one theory but can combine elements across theories in ways that resonate with our teaching styles and reflect our best understanding of our students. For instance, a teacher might draw on elements of cognitivism to enhance students’ retention and recall but also develop group activities that promote social constructivism through peer-to-peer communication. Especially with younger children, instructors might draw on behaviorism by using rewards and positive reinforcement to motivate student engagement with the content, but also integrate humanism by empathizing with students and use constructive feedback to encourage a growth mindset. We can use our understanding of developmental stages to create lessons and activities that provide an appropriate level of challenge to help students grow in their understanding. Ultimately, we should view learning theories as guidelines, not rules, and draw on them in ways that reflect our own values and understandings.
Keeping this idea of learning across theories in mind, we can sum up the key takeaways from this chapter:
- Learning is the change in knowledge, behavior, or understanding that occurs when people make connections between new information and their existing knowledge. Various theories attempt to describe the factors that enable the learning process.
- Learning does not happen in the same way or at the same time for all students. Understanding developmental stages can help instructors align instruction with student readiness. Adult learners may have needs and constraints that differ from younger learners.
- The learning process is influenced by internal factors such as the student’s level of motivation and feelings of self-efficacy, and external factors such as the classroom environment and the adults and peers with whom the learner interacts.
- Instructors can take steps to foster better learning, including:
- Creating a democratic, empathetic, and supportive learning environment
- Assisting students in becoming self-directed learners and enhancing their motivation by offering a sense of control and choice in their learning
- Acknowledging that learning can be challenging, and helping students develop the mindset and self-efficacy that will support their persistence
- Offering regular and meaningful feedback
Suggested Readings
Brown, P. C., Roediger, H. L. III, & McDaniel, M. A. (2014). Make it stick: The science of successful learning. Belknap Press.
Brown, Roediger, and McDaniel present an engaging and accessible overview of current research in cognitive psychology. In addition to the science, the authors offer clear examples of how recommended recall and retrieval practices can be integrated into teaching.
Cooke, N. A. (2010). Becoming an andragogical librarian: Using library instruction as a tool to combat library anxiety and empower adult learners. New Review of Academic Librarianship, 16(2), 208-227. https://doi.org/10.1080/13614533.2010.507388
This article offers a thorough overview of andragogy and the characteristics and motivators of adult learners and offers library-specific advice for teaching adult students.
Curtis, J. A. (2019). Teaching adult learners: A guide for public librarians. Libraries Unlimited.
Curtis provides a clear introduction to andragogy to contextualize instruction in public libraries. She also addresses issues of culture and generational differences in teaching adults. Covering many aspects of instruction, including developing learning objects and teaching online, this book is valuable as one of the few to focus exclusively on issues of teaching and learning in public libraries.
Dweck, C. S. (2016). Mindset: The new psychology of success (Updated ed.). Penguin Random House.
In this book, Dweck defines fixed and growth mindsets and how they can influence people’s feelings of motivation and self-efficacy in learning. She also offers guidance on how to facilitate the development of a growth mindset for better learning.
Freire, P. (2000). Pedagogy of the oppressed (30th Anniversary Edition). Bloomsbury.
In this foundational work, Freire presents the concept of the banking model of education. This book provides a social justice foundation for a humanistic approach to education.
Merriam, S. B., & Bierema, L. L. (2014). Adult learning: Linking theory and practice. Jossey-Bass.
The authors provide a clear, concise, and engaging overview of both traditional and current theories of adult learning. The book includes activities and concrete examples for implementing the theories in the classroom.
Roy, L., & Novotny, E. (2000). How do we learn? Contributions of learning theory to reference services and library instruction. Reference Librarian, 33(69/70), 129-139. https://doi.org/10.1300/J120v33n69_13
The authors provide an overview of some of the major learning theories, followed by specific ideas and advice for applying the theory to reference and library instruction.
Svinicki, M. D. (2004). Learning and motivation in the postsecondary classroom. Bolton, MA: Anker Publishing.
This book takes a student-centered approach to describing learning theory. Chapter 7 provides an excellent overview of motivation and self-efficacy, including implications for practice.
References
Bartle, S. M. (2019). Andragogy. In Salem press encyclopedia. EBSCO.
Brown, P. C., Roediger, H. L. III, & McDaniel, M.A. (2014). Make it stick: The science of successful learning. Belknap Press.
Clark, K. R. (2018). Learning theories: Cognitivism. Radiologic Technology, 90(2), 176-179.
Clouse, B. (2019). Jean Piaget. In Salem press biographical encyclopedia. EBSCO.
Codington-Lacerte, C. (2018). Cognitivism. Salem press encyclopedia. EBSCO.
Dweck, C. S. (2015, September 22). Carol Dweck revisits the “growth mindset.” Education Week, 35(5), 20-24. https://www.edweek.org/ew/articles/2015/09/23/carol-dweck-revisits-the-growth-mindset.html
Dweck, C. S. (2016). Mindset: The new psychology of success (Updated ed.). Penguin Random House.
Flair, I. (2019). Zone of proximal development (ZPD). Salem press encyclopedia. EBSCO
Freire, P. (2000). Pedagogy of the oppressed (30th Anniversary Edition). Bloomsbury.
Gagné, R. M. (1985). The conditions of learning and theory of instruction. Wadsworth Publishing.
Heick, T. (2019, October 28). The assimilation vs accommodation of knowledge. teachthought. https://teachthought.com/learning/assimilation-vs-accommodation-of-knowledge/
Jensen, R. (2018). Behaviorism. Salem press encyclopedia of health. EBSCO.
Knowles, M. S. (1988). The modern practice of adult education: From pedagogy to andragogy. Revised and updated. Cambridge, The Adult Education Company.
Kretchmar, J. (2019a). Constructivism. Salem press encyclopedia. EBSCO.
Kretchmar, J. (2019b). Gagné’s conditions of learning. Salem press encyclopedia. EBSCO.
Kuhlthau, C. C. (1990). The information search process: From theory to practice. Journal of Education for Library and Information Science, 31(1), 72-75. https://doi.org/10.2307/40323730
Lucas, C. J. (1996). Humanism. In J. J. Chambliss (Ed.), Philosophy of education: An encyclopedia. Routledge.
Madsen, S. R., & Wilson, I. K. (2012). Humanistic theory of learning: Maslow. In N. M. Seel (Ed.), Encyclopedia of the Sciences of Learning. Springer.
Maslow, A. H. (1943). A theory of human motivation. Psychological Review, 50(4), 370-396.
McLeod, S. A. (2015). Cognitive approach in psychology. Simply Psychology. http://www.simplypsychology.org/cognitive.html
Mellon, C. A. (1986). Library anxiety: A grounded theory and its development. College & Research Libraries, 47(2), 160-165. https://doi.org/10.5860/crl.76.3.276
Mercadal, T. (2018). Social constructivism. Salem press encyclopedia. EBSCO.
Merriam, S. B., Caffarella, R. S., & Baumgartner, L. M. (2007). Learning in adulthood: A comprehensive guide (3rd edition). Wiley.
Perry, W. G., Jr. (1970). Forms of intellectual and ethical development in the college years; A scheme. Holt.
Popp, J. A. (1996). Learning, theories of. In J. J. Chambliss (Ed.), Philosophy of education: An encyclopedia. Routledge.
Roth, A. L. (2018). Pierre Bourdieu. Salem press biographical encyclopedia. EBSCO.
Shaffer, R. H. (2006). Key concepts in developmental psychology. Sage UK.
Sharp, A. (2012). Humanistic approaches to learning. In N.M. Seel (Ed.), Encyclopedia of the Sciences of Learning. Springer.
Skinner, B. F. (1938). The Behavior of organisms: An experimental analysis. Appleton-Century.
Svinicki, M. D. (2004). Learning and motivation in the postsecondary classroom. Anker Publishing.
Zucca-Scott, L. (2010). Know thyself: The importance of humanism in education. International Education, 40(1), 32-38.



